LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a revolutionary technology that has transformed our ability to accurately map and understand the physical world. It uses laser light to measure distances to the Earth's surface, offering precise three-dimensional information about the shape and contours of the terrain and structures.
At its core, LiDAR technology involves emitting laser beams towards the ground or other targets and measuring the time it takes for the light to return after bouncing off the surface. This time, known as the time of flight, is then converted into distance measurements, allowing for the creation of detailed three-dimensional representations of the scanned area.
LiDAR systems consist of several key components: a laser to emit the light, a scanner to direct the laser beams across the target area, and a specialized GPS receiver to accurately track the location and elevation of the LiDAR device itself. Whether mounted on aircraft, drones, satellites, or ground-based platforms, these components work in unison to capture high-resolution topographic data.
The beauty of LiDAR lies in its ability to penetrate dense vegetation and other obstructions, enabling it to reveal the ground surface underneath. This capability makes LiDAR an indispensable tool in various fields, from archaeology, where it can uncover hidden structures beneath forest canopies, to urban planning and disaster management, where it helps in designing resilient infrastructures and assessing risks.
LiDAR's versatility extends across numerous disciplines, demonstrating its significance in both scientific research and practical applications:
Environmental Science and Conservation: LiDAR is pivotal in monitoring forest canopy density, assessing biomass, and mapping flood zones. It plays a critical role in wildlife habitat conservation by providing detailed topographic data that helps in understanding the natural landscape.
Archaeology and Historical Preservation: By revealing minute topographical changes invisible to the naked eye, LiDAR has led to the discovery of ancient settlements, road systems, and architectural ruins, offering new insights into human history.
Urban Planning and Civil Engineering: Urban planners utilize LiDAR data to design cities with precise elevations, optimize land use, and enhance transportation systems. It also aids engineers in constructing bridges, roads, and other infrastructures by providing accurate terrain models.
Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics: In the realm of autonomous technology, LiDAR sensors are crucial for obstacle detection and navigation. They enable self-driving cars to "see" their surroundings in three dimensions, ensuring safe and efficient travel.
Related Reading: 10 Common LiDAR Applications
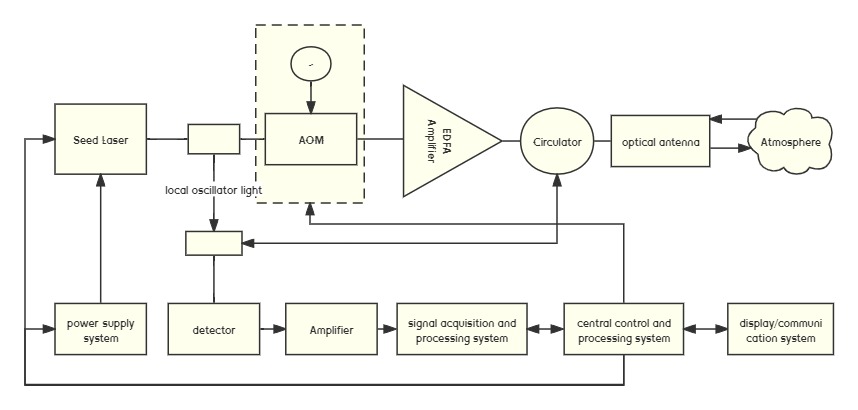
The light sources utilized in LiDAR technology are, inherently, lasers, which predominantly operate within two specific wavelengths: 905nm and 1550nm. The 905nm wavelength frequently makes use of Edge-Emitting Lasers (EEL) and Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (VCSEL). In contrast, the 1550nm wavelength typically requires the implementation of Fiber Lasers.

Need A Pulsed Fiber Laser as the LiDAR Laser Source?
Related Readings:LiDAR Comparison: 905nm vs. 1550nm
Wavelength: Determines the beam's penetration capability and reflectivity on different materials.
Power: Determines the detection range and the minimum detectable reflectivity of the target.
Pulse Width: Affects resolution and accuracy.
Repetition Rate: Determines the data update rate and the maximum measurement distance.
Beam Quality: Influences the laser's focusing ability and propagation stability.
Divergence Angle: Determines whether the light is compact and affects detection performance.
Stability and Reliability: Power and wavelength stability under different working conditions.
LiDAR imaging methods vary widely due to different combinations of light sources, ranging principles, detectors, and beam manipulation techniques. These methods can generally be divided into scanning and non-scanning types. For more detailed information, you might want to read further from the source.
Contact: Lumispot
Phone: +86-15072320922
Tel: +86-510-87381808
Email: sales@lumispot.cn
Add: Bldg 4 No.99 Fu Rong 3rd Road, Wuxi, China