In modern optoelectronic technology, semiconductor lasers stand out with their compact structure, high efficiency, and fast response. They play an essential role in fields such as communications, healthcare, industrial processing, and sensing/ranging. However, when discussing the performance of semiconductor lasers, one seemingly simple yet extremely important parameter—the duty cycle—is often overlooked. This article dives into the concept, calculation, implications, and practical significance of duty cycle in semiconductor laser systems.
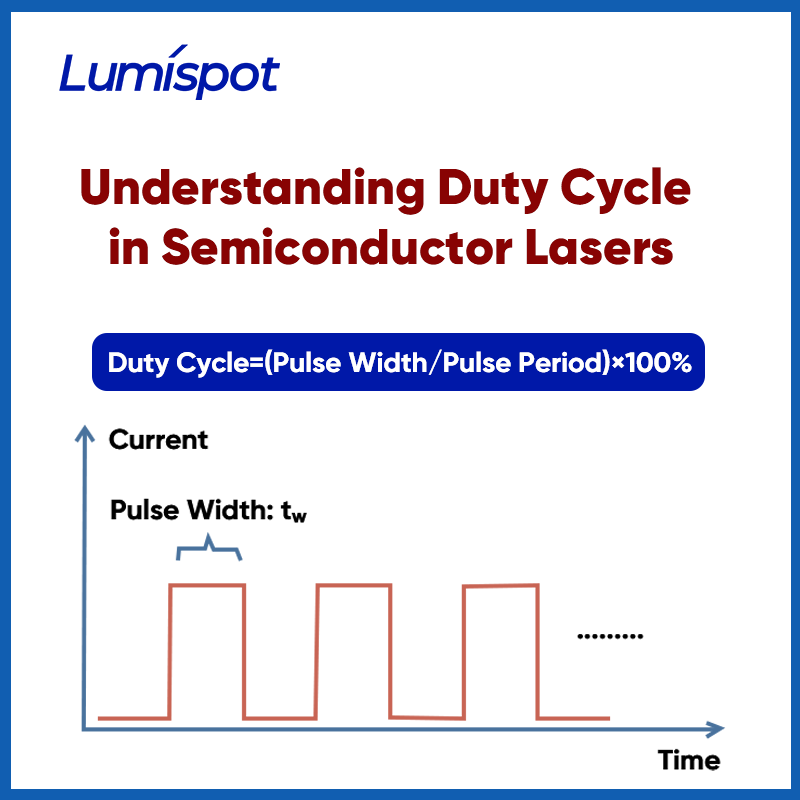
1. What Is Duty Cycle?
Duty cycle is a dimensionless ratio used to describe the proportion of time a laser is in the “on” state within one period of a repeating signal. It is typically expressed as a percentage. The formula is: Duty Cycle=(Pulse Width/Pulse Period)×100%. For example, if a laser emits a 1-microsecond pulse every 10 microseconds, the duty cycle is: (1 μs/10 μs)×100%=10%.
2. Why Is Duty Cycle Important?
Although it’s just a ratio, the duty cycle directly affects the laser’s thermal management, lifespan, output power, and overall system design. Let’s break down its significance:
① Thermal Management and Device Lifetime
In high-frequency pulsed operations, a lower duty cycle means longer “off” times between pulses, which helps the laser cool down. This is especially beneficial in high-power applications, where controlling the duty cycle can reduce thermal stress and extend device life.
② Output Power and Optical Intensity Control
A higher duty cycle results in greater average optical output, while a lower duty cycle reduces the average power. Adjusting the duty cycle allows for fine-tuning of output energy without changing the peak drive current.
③ System Response and Signal Modulation
In optical communication and LiDAR systems, the duty cycle directly influences response time and modulation schemes. For instance, in pulsed laser ranging, setting the right duty cycle improves echo signal detection, enhancing both measurement accuracy and frequency.
3. Application Examples of Duty Cycle
① LiDAR (Laser Detection and Ranging)
In 1535nm laser ranging modules, a low-duty-cycle, high-peak pulse configuration is typically used to ensure both long-range detection and eye safety. Duty cycles are often controlled between 0.1% and 1%, balancing high peak power with safe, cool operation.
② Medical Lasers
In applications like dermatological treatments or laser surgery, different duty cycles result in different thermal effects and therapeutic outcomes. A high duty cycle causes sustained heating, while a low duty cycle supports instantaneous pulsed ablation.
③ Industrial Material Processing
In laser marking and welding, the duty cycle affects how energy is deposited into materials. Adjusting the duty cycle is key to controlling engraving depth and welding penetration.
4. How to Select the Right Duty Cycle?
The optimal duty cycle depends on the specific application and laser characteristics:
① Low Duty Cycle (<10%)
Ideal for high-peak, short-pulse applications like ranging or precision marking.
② Medium Duty Cycle (10%–50%)
Suitable for high-repetition pulsed laser systems.
③ High Duty Cycle (>50%)
Approaching continuous wave (CW) operation, used in applications like Optical Pumping and communications.
Other factors to consider include thermal dissipation capability, driver circuit performance, and the laser’s thermal stability.
5. Conclusion
Though small, the duty cycle is a key design parameter in semiconductor laser systems. It affects not only performance output but also the long-term stability and reliability of the system. In future laser development and application, precise control and flexible use of duty cycle will be crucial to enhancing system efficiency and enabling innovation.
If you have more questions about laser parameter design or applications, feel free to reach out or leave a comment. We're here to help!
Contact: Lumispot
Phone: +86-15072320922
Tel: +86-510-87381808
Email: sales@lumispot.cn
Add: Bldg 4 No.99 Fu Rong 3rd Road, Wuxi, China